An NGO’s Internal Trustee Report is a vital document compiled typically by senior management or C-suite. It’s main objective is to provide the trustees with a snapshot of the organisation’s activities, accomplishments, and financial position for a given period (typically quarterly, bi-yearly or annually).
The report is used as an accountability and transparency tool, keeping the Trustees informed of key activities performed by the charity. Understanding its importance in governance and regulatory compliance, we have compiled this article that offers some key elements you may want to include in your next Internal Trustee Report. Let’s dive in!
To download the free editable Trustee Report template, click the button below:
Purpose of an Internal Trustee Report
The Trustee Report has several key objectives:
- Ensures accountability and transparency by detailing activities and finances.
- Guides strategic planning and decision-making.
- Helps Trustees make smart, informed strategic decisions.
Components of an Internal Trustee Report:
The content of the Trustee Report will vary widely depending on the nature and size of your charity, but commonly includes the following sections:
1. Executive Summary
As the name suggests, the executive summary offers a quick glimpse of what’s included in the Internal Trustee Report for the reporting period:
- Key achievements and milestones
- Summary of financial performance
- Highlight impact and outcomes
2. Financial Management Report
The finance section, either standalone or integrated within the Internal Trustee Report, offers a synopsis of the organisation’s financial status and management practices during the reporting period. It furnishes vital insights into the charity’s financial health, focusing on goals, objectives, and progress.
It is typical for charities to show budgeted figures in the same section with their actual income and expenditure during a specific reporting period. This section typically covers:
- Budgeted projections and planned allocations for income and expenditure categories, such as administrative and fundraising costs.
- Actual income sources like donations, grants, program revenues, etc and expenditures incurred.
- Comparison of budgeted and actual figures, highlighting variances.
- Reasons for significant variances, such as unexpected income or expenses, changes in funding sources, shifts in programmatic priorities, etc.
Here, you’ll find a brief analysis of an NGO’s income sources, such as donations, grants, and expenses:
Additionally, this report may present key financial ratios to assess the organisation’s liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. Concise snapshots on reserves, fund balances, investments and compliance with financial regulations further enhance the trustees’ understanding of the charity’s financial health and governance.
3. Projects Department Update
As the name suggests, this section gives trustees a quick snapshot of the organisation’s project/programme activities. A selection of the following details give an insight into the effectiveness of the organisation’s project implementation:
- Summary of Projects: No. of projects implemented by the organisation during the reporting period.
- Summary of Impact: Information on projects completed during the reporting period and outcomes and their impact on beneficiaries or target communities (linked to the organisation’s high-level KPIs).
- Program Highlights: A high-level update on the no. of ongoing/upcoming programs, if necessary, including progress made and challenges encountered only for major high-value projects.
4. Fundraising Department Update
The Fundraising Department offers trustees an overview of the organisation’s fundraising efforts, performance highlights, and strategies in this section.
- Income Overview: An overview of the fundraising income generated by the organisation, covering the amount/number of donations, grants, sponsorships, and other fundraising activities.
- Challenges and Opportunities: Identification of major challenges the fundraising department faces and opportunities for improvement or expansion.
- Future Plans: Brief outline of future fundraising initiatives, including goals, targets, and planned activities.
5. Marketing & Advocacy Update
This part of an NGO’s Internal Trustee Report details marketing activities. It provides an overview of the marketing initiatives and campaigns implemented. These could be related to digital marketing, advocacy, and traditional marketing efforts like print media.
- Audience Engagement: A snapshot of the organisation’s efforts to engage with its target audience, including strategies for reaching new supporters, retaining existing donors, and building mission awareness.
- Impact Metrics: Analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to marketing activities. This is likely to be high-level for the Trustees.
- Success Stories: Highlighting successful marketing campaigns or initiatives that have effectively promoted the organisation’s mission, attracted donors, or raised awareness about its programs and impact.
Here, you might also include major challenges, opportunities, and future goals for the marketing department.
6. Operations Department Update
The Operations Department update covers human resources (HR), compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and other operational updates.
- Human Resources (HR) Updates: Information on staffing changes, upcoming senior recruitment, or ongoing investigations/legal challenges.
- Compliance and Regulatory Updates: Updates on compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Also, any changes in regulatory requirements affecting the organisation’s operations.
- Data Protection and Security: Key highlights on data protection measures and cybersecurity initiatives to ensure the security and integrity of the organisation’s data and systems.
- Operational Efficiency: Significant updates to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and optimise resources within the organisation’s operations, such as implementing new technologies.
Note: It’s worth noting that much of the above information may be reported ‘by exception’. In other words, where activities are considered business as usual, they will not necessarily be reported to the Trustees or senior management. However, any variances above organisational thresholds will be.
7. Ecological Impact Update
The environmental impact section gives trustees insights into the organisation’s efforts to minimise its carbon footprint while promoting sustainability.
- Environmental Policy and Compliance: Outline the NGO’s commitment to environmental sustainability, conservation, and responsible resource management. Summarise the organisation’s compliance with relevant environmental regulations, laws, initiatives, and standards, like SECR in the UK.
Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) is a UK government initiative that advises certain organisations, including large companies and charities, to report on their energy use, greenhouse gas emissions, and energy efficiency measures.
Refer to these Charity Commission’s guidelines for SECR reporting.
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Reporting: Statistics of the organisation’s environmental footprint, including assessments of energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts associated with its operations.
- Environmental Initiatives: List of environmental initiatives and programs implemented by the organisation to minimise its environmental impact and promote sustainability.
8. Risk Management
This section aids in making informed decisions to safeguard the organisation’s interests. We suggest the identification of the top 5 risks based on probability and impact, highlighting mitigation measures and responsible parties for risk management. Key areas to cover here include the following:
- Identification of Risks: Potential risks and uncertainties that may impact the organisation’s operations, programs, finances, reputation, or stakeholders.
- Risk Analysis: Indication of the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks.
- Mitigation Strategies: Short description of strategies, measures, and controls implemented to mitigate or manage identified risks.
- Responsibilities and Accountability: Mention roles, responsibilities, and accountability for specific risk management within the charity. Also, highlight any changes to the internal risk framework model (See below).

In addition, this section might include details on emerging risks and proactive measures to anticipate and address these risks effectively.
9. Safeguarding
This section covers the organisation’s commitment to ensuring the safety and well-being of its staff, beneficiaries, and stakeholders, as well as its efforts to maintain a culture of transparency, accountability, and integrity.
- Implementation Framework: Summary of how safeguarding strategies are implemented throughout the organisation during the reporting period, including training programs, reporting mechanisms, and monitoring processes.
- Incident Reporting: Document any safeguarding incidents or concerns reported during the reporting period, along with specifics of the organisation’s response and resolution processes.
10. Security Report
This part of an NGO’s Internal Trustee Report talks about the charity’s efforts to ensure the security and protection of its assets, operations, and stakeholders (this may be more applicable to International charities working in high-risk zones). It helps trustees understand the organisation’s resilience against security threats and risks.
It generally covers the following:
- Incident Reporting: Documentation of security incidents or breaches (including aid diversion issues, particularly for INGOs operating in high-risk areas) that occurred during the reporting period. Highlights such as the nature of the incident, impact, response measures taken, and outcomes are provided here.
- Threat Assessment: Brief analysis of potential security threats and vulnerabilities the organisation faces, including physical security risks, cyber threats, and other security concerns.
Furthermore, recommendations and action plans for the future are also touched upon.
11. Amendments to Policies Reserved by the Board
In this section, charities clarify that trustees hold responsibility for policies and procedures. It’s common to find the following details here:
- Policy Updates: Identify any amendments, revisions, or updates to organizational policies and procedures during the reporting period.
- Policy Ratification: Updates on the board’s review and approval of policy changes, ensuring alignment with organisational goals and governmental and trust policies.
Appendices:
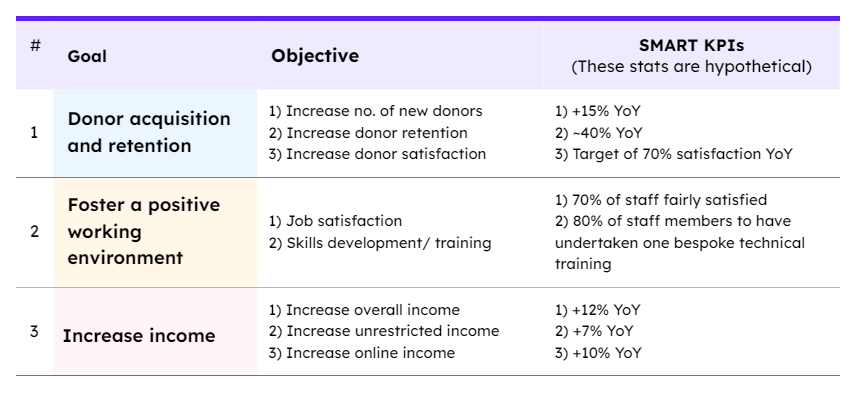
A) Reporting on Organisational Key Performance Indicators
Lastly, an effective trustee report presents KPI data related to the strategic goals of the organisation. Examples of these KPIs are as follows:
Download the Trustee Report Template (Editable Word File)
Download the editable template for compiling your next Internal Trustee Report below.